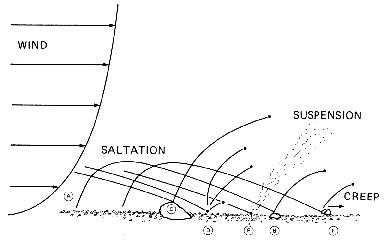
 Diagram
showing the three principal modes of aeolian transport of grains:
surface shear stress exerted by the wind causes grain (A) to lift off
the surface, carries it downwind back to the surface where it bounces
(B) back into flight; this motion is termed saltation; grain
at (C) hits a large rock - possibly causes some erosion - and
elastically rebounds to a relatively high saltation trajectory; grain
at (D) strikes the surface and "triggers" other grains into
saltation; grain at (E) strikes the surface containing very fine
particles (too fine to be moved by the wind alone in this case) and
sprays them into the wind where they are carried by turbulence in
suspension; grain at (F) strikes larger grain and pushes it
downwind a short distance in a mode of transport termed impact
creep, or traction.
Diagram
showing the three principal modes of aeolian transport of grains:
surface shear stress exerted by the wind causes grain (A) to lift off
the surface, carries it downwind back to the surface where it bounces
(B) back into flight; this motion is termed saltation; grain
at (C) hits a large rock - possibly causes some erosion - and
elastically rebounds to a relatively high saltation trajectory; grain
at (D) strikes the surface and "triggers" other grains into
saltation; grain at (E) strikes the surface containing very fine
particles (too fine to be moved by the wind alone in this case) and
sprays them into the wind where they are carried by turbulence in
suspension; grain at (F) strikes larger grain and pushes it
downwind a short distance in a mode of transport termed impact
creep, or traction. aus: Greeley, R. & Iversen, J.D. (1985), p. 17